Modulus of a complex number The modulus of a complex number z=aib (where a and b are real) is the positive real number, denoted z , defined by z = a 2 b 2 The complex_modulus function calculates the module of a complex number online For the calculation of the complex modulus, with the calculator, simply enter the complex number inTo draw a graph of f(x) draw the graph of f(x) for x>0 and then its mirror image with respect to y axis to draw f(x) draw the complete graph of f(x) and then the portion of the graph for which f(x)Join up the points in a straight line manner;

The Tangent Function Functions Siyavula
Modulus tan 2x graph
Modulus tan 2x graph-Y = 3*x^4 2 * x^3 7 * x^2 2 * x 9;Graph of the Modulus Function DoubleRootin 12 Graph (Part 2) In this lesson, we'll learn how to plot the graphs of functions like x – 4, x 1, 2x – 1, etc To plot these, we'll use the definition again, just like we did for x Let's start with the first one
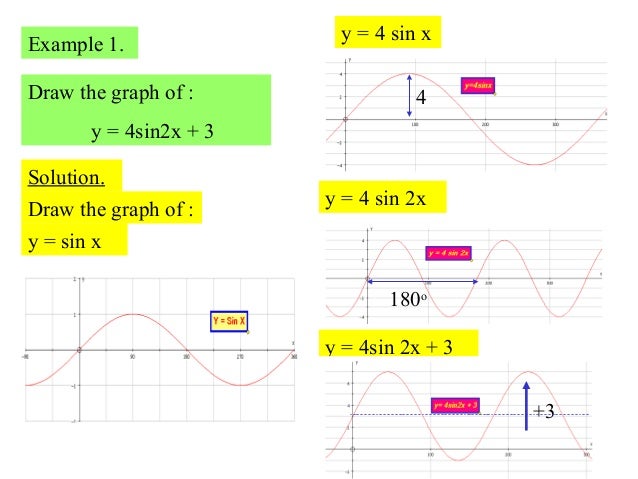


Drawing Trigonometric Graphs
Get answer iff(x)=(sinx),(sqrt(1tan^2x))(cosx),(sqrt(1cot^2x)), then find the range of f(x)Enter Graph Equations f(x)= f(x)= f(x)= f(x)= f(x)= f(x)= Settings X Range to ;MATH SOLVER polynomial solver 2x – 3 = 0 (linear) 3x² 4x 8 = 0 (quadratic) 5x³ 2x² – 4x 2 = 0 (cubic) 7x⁴ – 2x³ 3x² 2x – 1 = 0 (quartic) system of linear equations solver;
Label Every Y ticks;With 2 unknown 2x – 9 = 9 3x 4y = 13 with 3 unknown5x 4y 2z = 4 7x 2y 3z = 19The modulus function y =│x│ The absolute value of x is defined as This always gives a positive result Example y=3x 2 6x2 has graph Whereas y=3x²6x−2 has graph Note how the negative portions have been reflected in the xaxis Example y = 3tanx y
Graphing Modulus Functions type "abs" to stand for modulus Submit wwwmrbartonmathscom Computing Get this widget Build your own widget » Browse widget gallery » Learn more » Report a problem » Powered by WolframAlpha Terms of useIf f(x) = tan x is a modulus function, show the function graphically;Consider x=f(y) But, modulus can not be equated to negative value Hence, x can not be negative It means we need to discard left half of the graph of inverse function y=f⁻¹(x) On the other hand, modulus of negative or positive value is always positive Hence, positive value of x=a correspond to two values of function in dependent variable, a=±f(y) Corresponding to these two
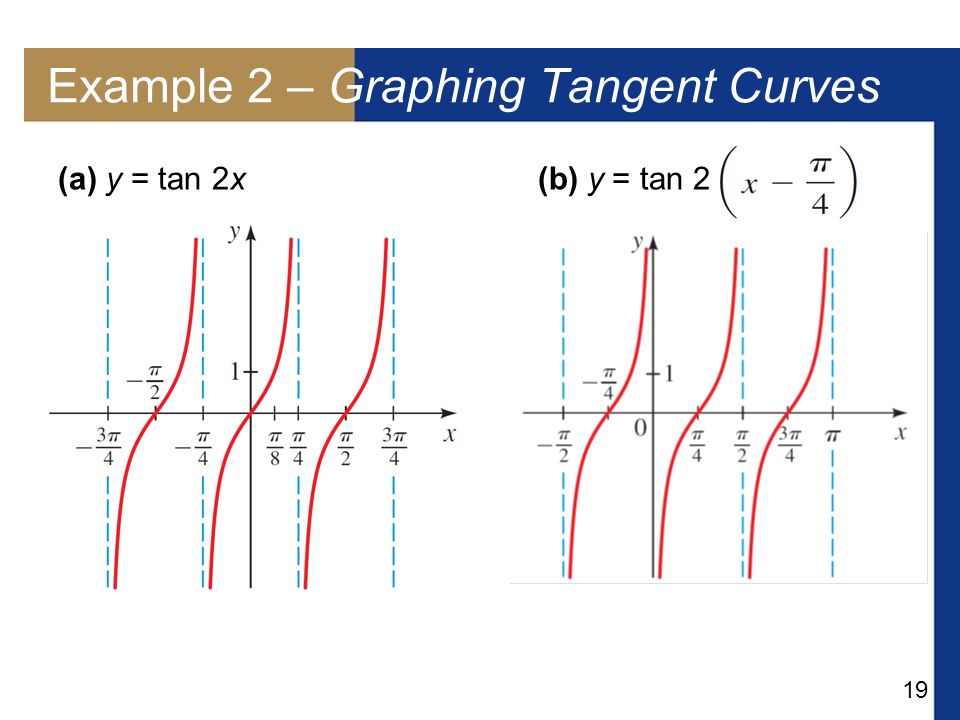


More Trigonometric Graphs Ppt Download



Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia
· Y = TAN X 5 Changing Trigonometric GraphsYou should know how the following graphs differ from the basictrigonometric graphsY= 2 SIN X The 2 in front of the sin x changes the "amplitude" of the graph 6 Y = 5 COS XAs expected the amplitude of the graph is now 5 Hence thegraph has a maximum value of 5 and a minimum value of –5 7Y Range to ;Here \(a\) is the \(x\)coordinate of the point of intersection, so we know it is a solution to \(2x1=\dfrac{1}{x}\) Multiplying this through by \(x\), we derive the quadratic equation \(2x^2x1=0\) This factorises to \((2x1)(x1)=0\), so the solutions are \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\) and \(x=1\) From the diagram we see that \(a\) is positive, so \(a=1\)



Graphs Of The Other Trigonometric Functions Algebra And Trigonometry
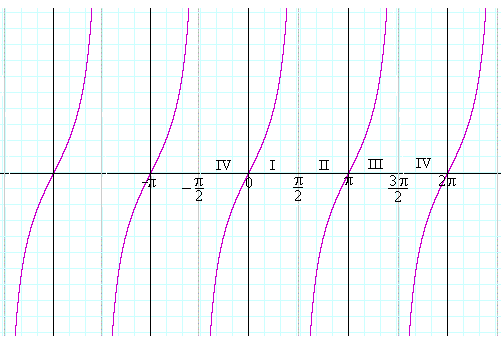


Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions
Tan θ= 0 when θ= 0˚, 180˚, 360˚ tan θ = 1 when θ= 45˚ and 225˚ tan θ = –1 when θ= 135˚ and 315˚ tan θdoes not have any maximum or minimum values The range of values of tanThis is how it would look like If you want an online graph plotter you can check this out link PS For the absolute value of x (mod in your terms) people online tend to use the keyword 'abs' instead of 'mod' 'mod' also stands for remainder oper2−2x−2 (d) fx()=x 2x1 (e) fx()=3x 2−4x2 (f) fx()=x 21 You should have noted that if the graph of the function either intercepts the xaxis in two places or touches it in one place then the solutions of the related quadratic equation are real, but if the graph does not intercept the xaxis then the solutions are complex
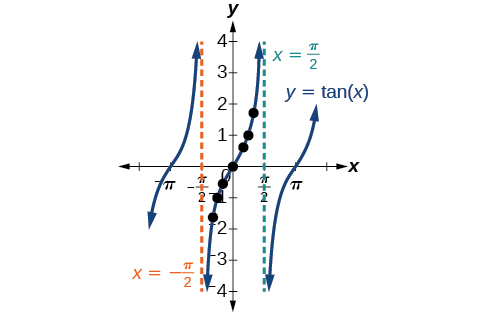


Graphs Of The Other Trigonometric Functions Algebra And Trigonometry



Tangent Graphs Worked Solutions Examples Videos
The absolute value is the distance between a number and zero The distance between 0 0 and 2 2 is 2 2 π 2 π 2 The vertical asymptotes for y = tan ( 2 x) y = tan ( 2 x) occur at − π 4 π 4, π 4 π 4, and every π n 2 π n 2, where n n is an integer x = π 4 π n 2 x = π 4 π n 2Cos(x^2) (x−3)(x3) Zooming and Recentering To zoom, use the zoom slider To the left zooms in, to the right zooms out When you let go of the slider it goes back to the middle so you can zoom more You can clickanddrag to move the graph around If you just clickandrelease (without moving), then the spot you clicked on will be the new center To reset the zoom to theHow to Check Continuity of Modulus Function Here we are going to how to examine the continuity of the modulus function To know the points to be remembered in order to decide whether the function is continuous at particular point or not, you may look into the page " How to Check Continuity of a Function If Interval is not Given "



Sketching The Graph Of 1 Tan 2x Pi 2 Youtube


Modulus Function
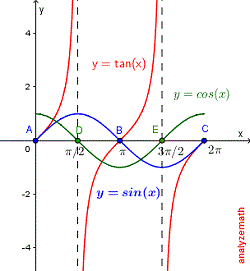
Tan 1(tan 6ˇ 5 ) = ? · Graphs of tan, cot, sec and csc by M Bourne The graphs of `tan x`, `cot x`, `sec x` and `csc x` are not as common as the sine and cosine curves that we met earlier in this chapter However, they do occur in engineering and science problems They are interesting curves because they have discontinuities For certain values of x, the tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant · Example 4 Draw the graph of sin(x) cos(x) in the interval x ϵ 0, π Solution sin(x) cos(x) = √2 sin(x π/4) First, make the graph of the function then take the modulus Here at the place of sinx we have √2 sin(x π/4) so, the graph will be of type sin x only but the graph will be starting from x = π/4 y = sin(x) cos(x)



Transformation Of Graphs By Modulus Function Functions Openstax Cnx



Graphs Of The Other Trigonometric Functions Algebra And Trigonometry
Show Grid Bold Labeled Gridlines Function Width pixels;Interactive, free online graphing calculator from GeoGebra graph functions, plot data, drag sliders, and much more! · Online Graphing Calculator Plot your own SVG Math Graphs You can plot 2 functions, function 1 (in dark green) and function 2 (in magenta) Edit your functions and then click the "Graph it" button below To remove a graph, leave its text box blank


What Is The Period Of The Function Tan 2x 6



Trigonometry Graphs For Sine Cosine And Tangent Functions
X Tick Distance Y Tick Distance Label Every X ticks;Graph of modulus function Lecture on Graph of modulus function by RAJNIKANT SIR , Lecture on Graph of modulus function by RAJNIKANT SIR , AboutPressCopyrightContactIf f(x) = x 2 2 is modulus, then plot the graph for this function


Tan Graph
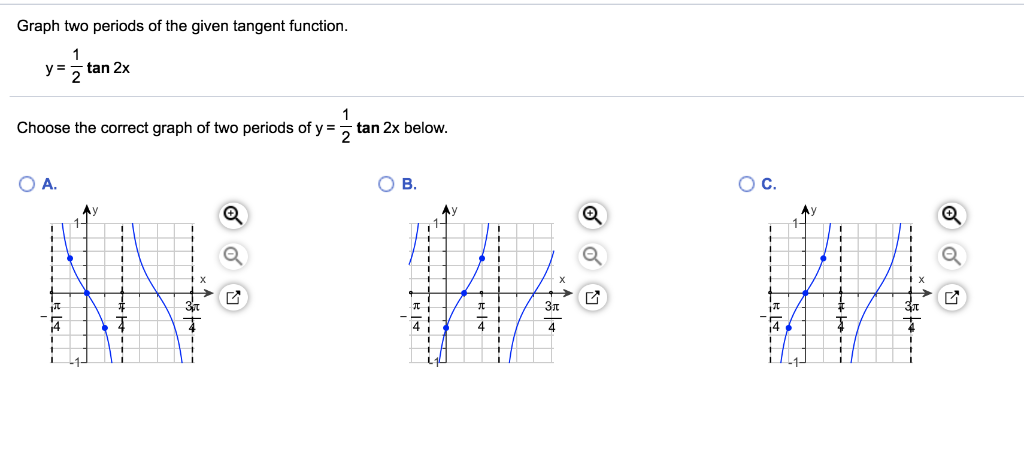


Solved Graph Two Periods Of The Given Tangent Function Y Chegg Com
· Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeIn mathematics, hyperbolic functions are analogues of the ordinary trigonometric functions, but defined using the hyperbola rather than the circleJust as the points (cos t, sin t) form a circle with a unit radius, the points (cosh t, sinh t) form the right half of the unit hyperbolaAlso, just as the derivatives of sin(t) and cos(t) are cos(t) and –sin(t), the derivatives of sinh(t) andLe graphe de la fonction montre la courbe de la fonction mathématique suivante "TAN (x)" Les fonctions suivantes sont disponibles π = pi () Valeur absolue = abs (x)1 Rond = runden (x) Au hasard = zufall ()2 Sine = sin (x)


Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions



6 Trigonometry Graph Example 3 Sketch Y Tan 2x Youtube
Critical points (ie x intercept(s), yintercept, turning point (if you are sketching a quadratic graph)) Let's take a look at the working of 2 different students Student A Sketch the modulus graph using table of values;Related » Graph » Number Line » Examples » Our online expert tutors can answer this problem Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutesU ceide nt ies r l ad to sin 2 x, cos ,2x, 3 o 3x d tan 3x, and apply them to simplify trigonometric equations 310 General olution f rigonomet c equations of the type sin = find theg ne ral solu ogonom tr c quat ns type sin = sin , cos = cos and tan = tan i nd g general soluti os f in , cos =s cos and tan = tan



Modulus Functions Solving Equations Edexcel A Level Maths Pure Revision Notes



Calculus I Common Graphs
Plot(x, y, 'r', x, g, 'g') When you run the file, MATLAB generates the following graph − Setting Axis Scales The axis command allows you to · Since you have learned all the details about modulus function and how to plot the graph for such functions, practice some questions given below based on it If y = 2x 1 is a modulus function, plot the graph for it; · Functions tan x and cot c have a period \Pi Inverse Trigonometric function or Inverse circular function The functions y=sin^{1}x (or Arc sin x), y=cos^{1}x (or Arc cos x), y=tan^{1}x (or Arc tan x), etc, are inverse to trigonometric functions sin x, cos x, tan x, etc are called Inverse Trigonometric function or Inverse circular function



Functions Graph Sketching Isaac Physics


6 Trigonometry Graph Example 3 Sketch Y Tan 2x Youtube
The graph of y = tan θ, for 0˚ ≤ θ ≤ 360˚ obtained is as shown Properties of the tangent function The curve is not continuous It breaks at θ = 90˚ and 270˚, where the function is undefined ;Radian measure and graphs of trig functions • radians to measure angles • length of an arc • area of a sector • area of a segment • graphs of sine, cos and tan • values of functions in four quadrants • surd values for functions • transformations of sin, tan and cos curvesCos 2(x) = 1cos(2x) 2 sin (x) = 1−cos(2x) 2 tan(x) = sin(2x) 1cos(2x) = 1−cos(2x) sin(2x) En posant t = tan x 2 pour x 6≡π 2π, on a cos(x) = 1−t2 1t 2, sin(x) = 2t 1t et tan(x) = 2t 1−t · Somme, différence et produit cos(p)cos(q) = 2cos pq 2 cos p−q 2 cos(p)−cos(q) = −2sin pq 2 sin p−q 2 sin(p)sin(q) = 2sin pq 2 cos p−q 2 sin(p)−sin(q) = 2cos pq 2 sin p−q 2 tan(p)tan



Modulus Functions Solving Equations Edexcel A Level Maths Pure Revision Notes


Graph Tangent And Cotangent
Copy, save, email screenshot;Here we are going to see, transformation of graphs of modulus function Reflection A reflection is the mirror image of the graph where line l is the mirror of the reflection (i) The graph y = −f(x) is the reflection of the graph of f about the xaxis (ii) The graph y = f(−x) is the reflection of the graph of f about the yaxisSketching the Modulus Function Welcome to advancedhighermathscouk A sound understanding of how to sketch the Modulus Function is essential to ensure exam success Study at Advanced Higher Maths level will provide excellent preparation for your studies when at university Some universities may require you Continue reading →



What Is The Graph Of Log X Quora


9 3 Non Differentiable Functions
· Truth of the sin2xcos2x=1, for all x Signs of trigonometric functions Domain and range of trignometric functions and their graphs Expressing sin (x±y) and cos (x±y) in terms of sin x, sin y, cos x & cos y and their simple application Deducing identities like the following Identities related to sin 2x, cos 2x, tan 2x, sin 3x, cos 3x andGraph of ln(x) ln(x) function graph Natural logarithm graph y = f (x) = ln(x) ln(x) graph properties ln(x) is defined for positive values of x ln(x) is not defined for real non positive values of x ln(x)Tan 01δ Storage modulus, MPa E" (loss modulus) Tan Delta E' (storage modulus) Temperature, C° Loss modulus, MPa 104 103 102 50 100 0 150 104 103 102 101 100 101 07 06 05 04 03 02 00 time Phase 0 < ø < π / 2 MTS Dynamic Characterization Experience With core competencies in force control and motion measurement, MTS is ideally suited to developing new


4 Graphs Of Tan Cot Sec And Csc



Mention The Period Of Tan 2x Brainly In
\tan ( x ) tan (x) Utiliser la définition de la tangente Utiliser la définition de la tangente \frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d}x}(\frac{\sin(x)}{\cos(x)}) d x d (cos (x) sin (x) ) Pour deux fonctions dérivables, la dérivée du quotient des deux fonctions est le dénominateur fois la dérivée du numérateur moins le numérateur fois la dérivée du dénominateur, le tout divisé par le dénoStudent B Sketch the modulus graph using a series of 2 other graphsA modulus function gives the magnitude of a number irrespective of its sign It is also called the absolute value function In this minilesson we will learn about the modulus function definition, calculating modulus for numbers, variables and polynomials along with solved examples and modulus function questions



Graphs Of The Other Trigonometric Functions Algebra And Trigonometry


6 3 2 Sketching Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions Part 1 Spm Additional Mathematics
· The Corbettmaths video on the modulus function Videos, worksheets, 5aday and much moreNow 6 ˇ 5 is not between ˇ 2 and 2, so just like with the Bad II for Sin and Cos, I add or subtract the period until I get an angle that is in the range of tan 1(x) For Sin and Cos, I add or subtract 2ˇbecause that is their period For Tan, I add or subtract ˇ, the period of tan(x) Here 6 ˇ 5 6ˇ= 5, so tan 1(tan ˇ 5) = ˇ 5Image Size by pixels;
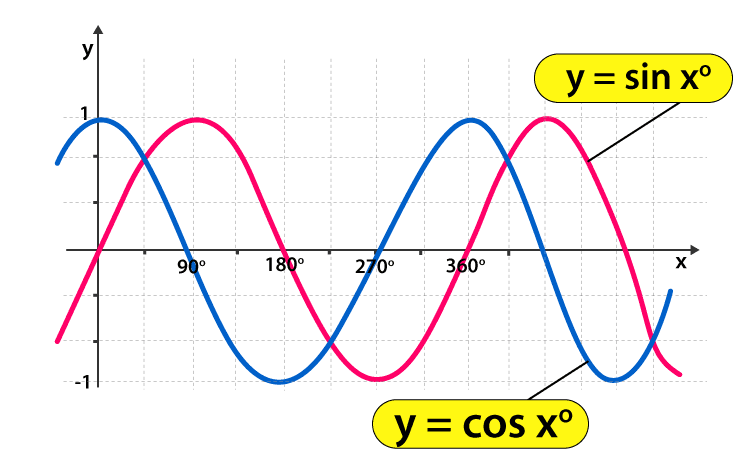


Trigonometry Graphs For Sine Cosine And Tangent Functions


What Is The Graph Of Mod Of Tan X Quora
· So, if you imagine the graph of f(x) = 2x1, if you only took the absolute value of your output, 2x1, you would reflect the negative part of your output in the xaxis in order to actually get the absolute value once you get to the point where 2x1 would be giving negative outputs In my head I go from right to leftG = 5 * x^3 9 * x 2;The graph of a modulus function is obtained by i) drawing the original function ii) reflecting in the xaxis any part of the function which is below the xaxis BEFORE AFTER AH Maths G Whyte 17 Functions and Graphs Example 5 Sketch the graphs of a) y = x b) y = x2 2 c) y = sin 2x x y x y x y x y x y x y AH Maths G Whyte 17 Functions and Graphs 1) f(x) = x 1 2) f(x) = 2x
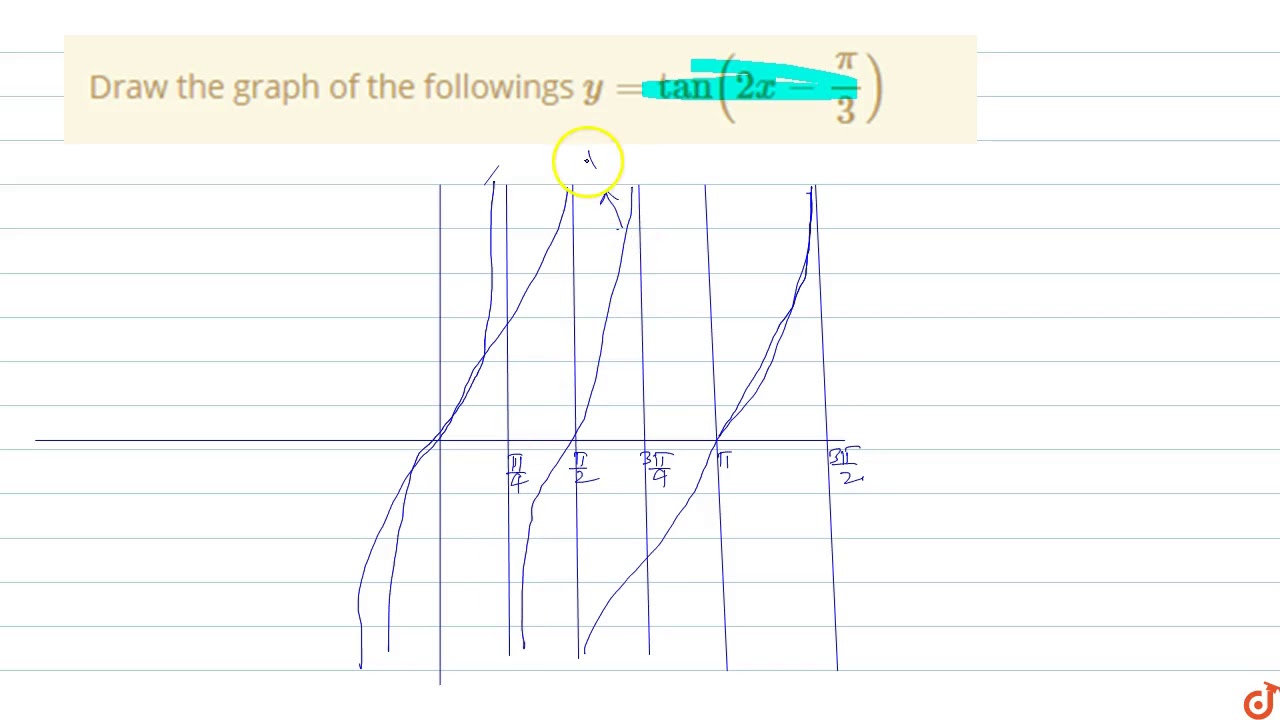


Draw The Graph Of The Followings Y Tan 2x Pi 3 Youtube
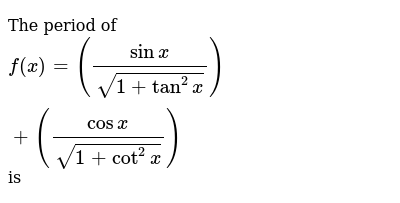


The Period Off X Sinx Sqrt 1 Tan 2x Cosx Sqrt 1 Cot 2
Polynomial, rational, modulus, signum, exponential, αlogarithmic and greatest integer functions, with their graphs Sum, difference, product and quotient of functions • Sets Selfexplanatory • Basic concepts of Relations and Functions Ordered pairs, sets of ordered pairs Cartesian Product (Cross) of two sets, cardinal number of a cross product Relations as an association between · the graph of function f is given below it has a vertical tangent at the point 3 comma 0 so 3 comma 0 has a vertical tangent let me draw that so it has a vertical tangent right over there and a horizontal tangent at the points 0 comma negative 3 0 comma negative 3 so as a horizontal tangent right over there and also has a horizontal tangent at 6 comma 3 so 6 comma 3 let me1)View SolutionHelpful TutorialsGraphing y=f(x)Translations of graphsReflections of graphsStretches of graphsPart



The Modulus Function Mathematics Learning And Technology



Transformation Of Graphs By Modulus Function Functions Openstax Cnx
About Beyond simple math and grouping (like "(x2)(x4)"), there are some functions you can use as well Look below to see them allRelated » Graph » Number Line » Examples » Our online expert tutors can answer this problem Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutesLet us draw the graph of two polynomials f(x) = 3x 4 2x 3 7x 2 2x 9 and g(x) = 5x 3 9x 2 Create a script file and type the following code − x = 10 001 10;



Solved Sketch The Graph Of The Function Include Two Ful Chegg Com



Transformation Of Graphs By Modulus Function Functions Openstax Cnx


Modulus Function



Graphs Of The Other Trigonometric Functions Algebra And Trigonometry
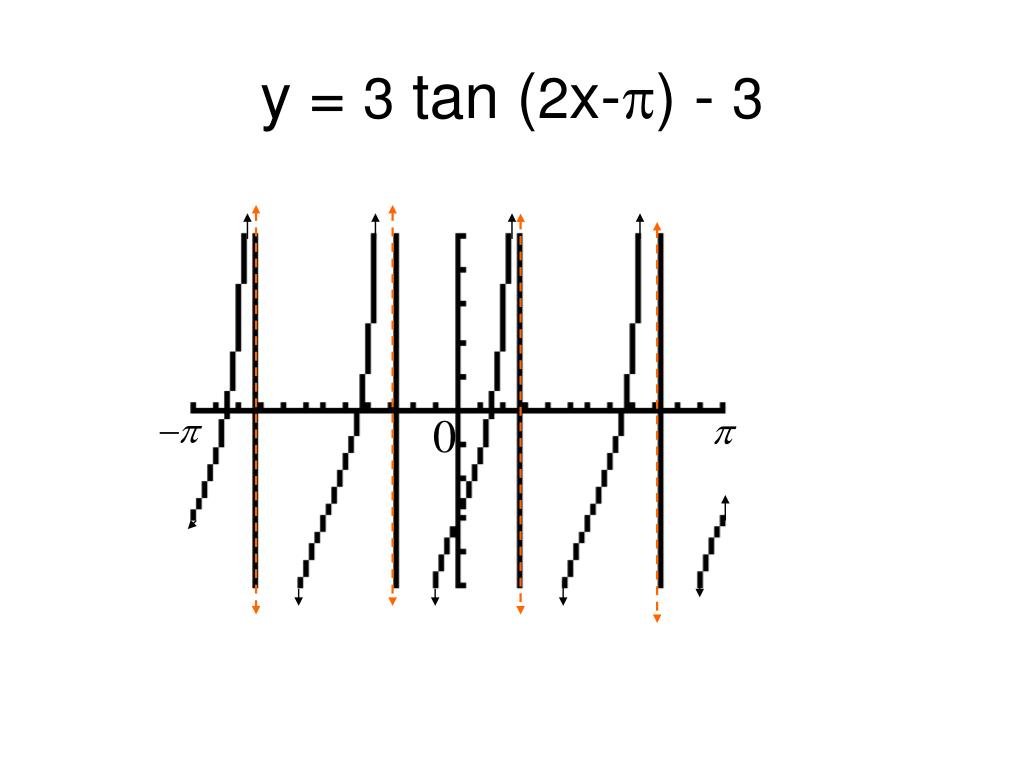


Ppt Graphing Tangent Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Transformation Of Graphs By Modulus Function Functions Openstax Cnx



Graph Y Tan 2x Youtube
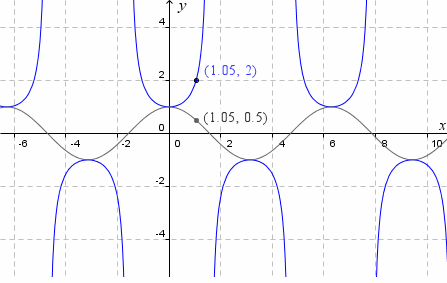


Explore The Slope Of The Tan Curve



Graphs Of The Circular Functions Ppt Download
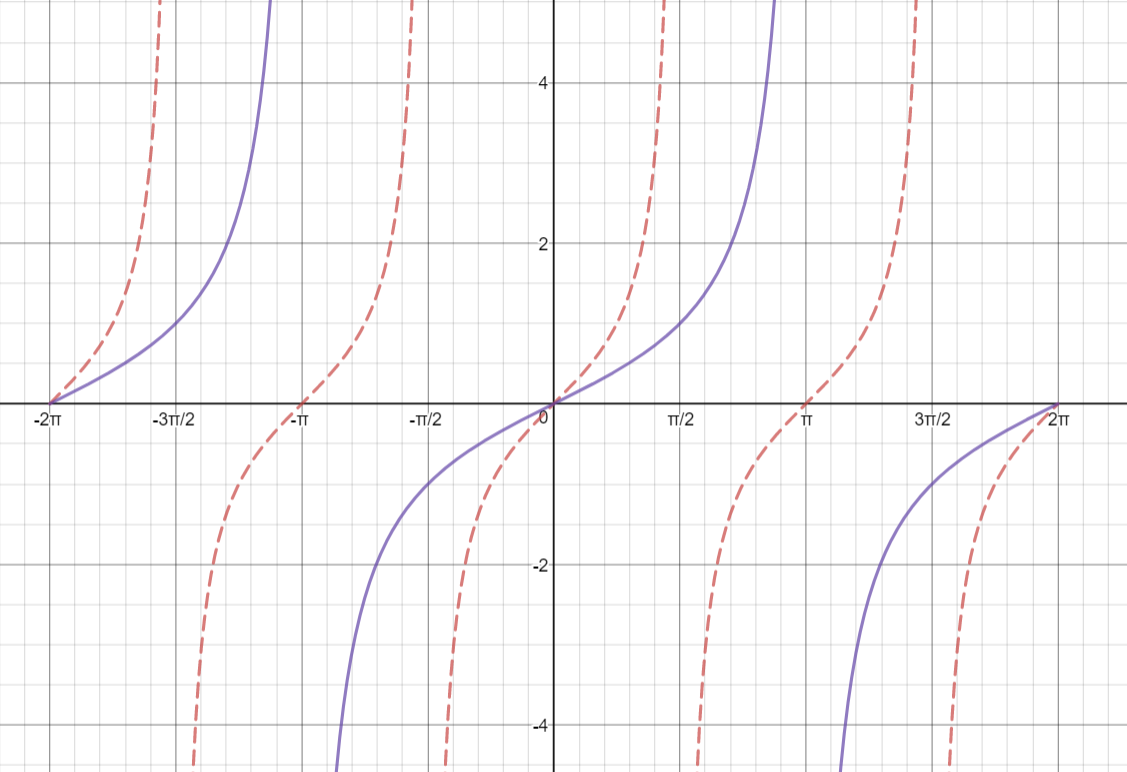


How Do You Graph Y Tan 1 2 X Socratic


Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions


What Is The Graph Of Mod Of Tan X Quora



The Derivative Of Tan 2x Derivativeit



08 01 Sketch Tan 2x 1 Youtube


What Is The Graph Of Mod Of Tan X Quora


4 Graphs Of Tan Cot Sec And Csc


Solution Y 2 Tan 2x Graph Two Periods Of The Given Tangent Function



6 Trigonometry Graph Example 3 Sketch Y Tan 2x Youtube


Draw Tangent Graph Y Tan X Mathematics
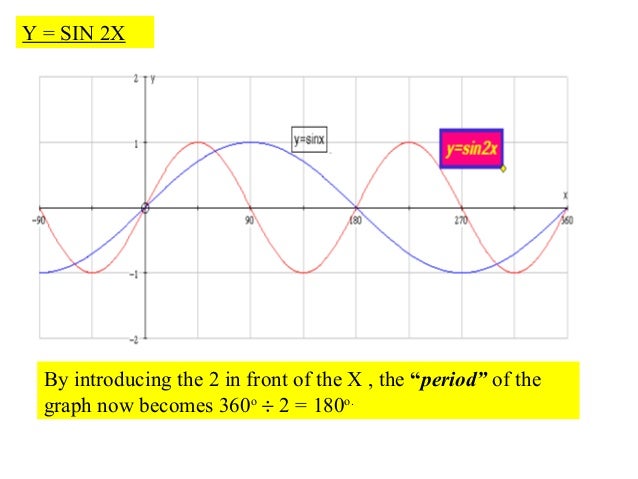


Drawing Trigonometric Graphs


What Is The Graph Of Mod Of Tan X Quora



The Tangent Function Functions Siyavula


Lambert W Function Wikipedia



Trigonometry



Periodic Functions Functions Openstax Cnx



The Tangent Function Functions Siyavula



Amplitude Period And Frequency Ck 12 Foundation


Drawing Trigonometric Graphs



Area Bounded By Y Tan X Y Tan 2x In Between X In Pi 3 Pi 3 I


4 Graphs Of Tan Cot Sec And Csc



The Tangent Function Functions Siyavula
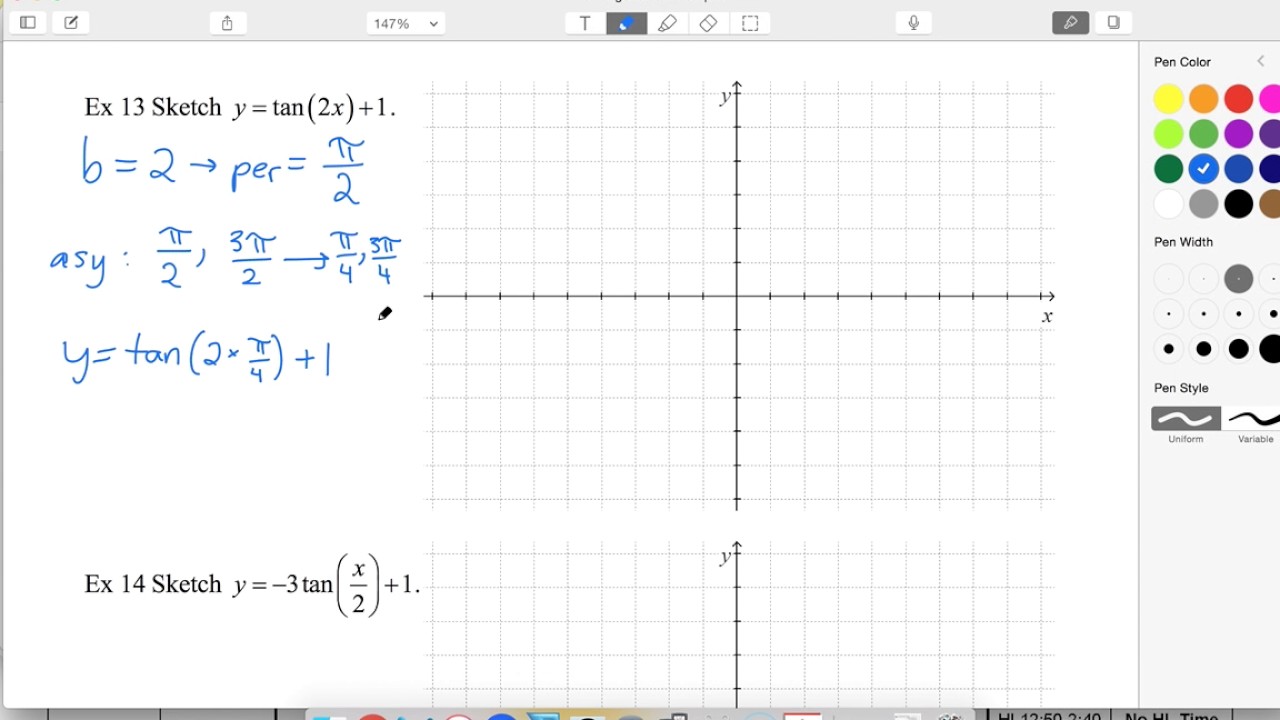


01 Ex13 Sketch Y Tan 2x 1 Youtube



How To Graph Tan Ex Y Tan2x Study Com
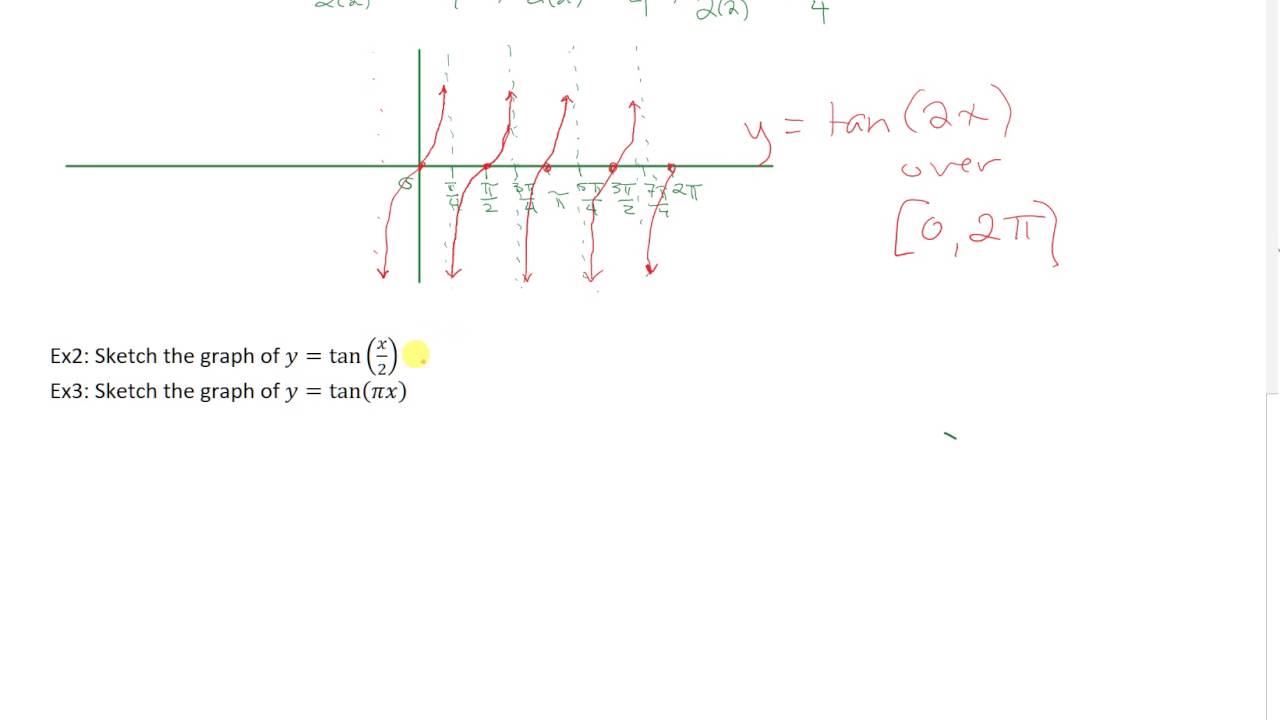


Sketching Y Tan 2x And Y Tan X 2 Youtube
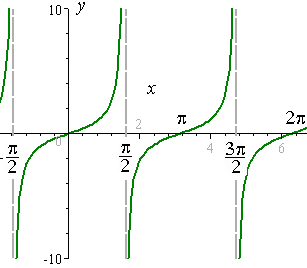


4 Graphs Of Tan Cot Sec And Csc



Modulus Function Functions Openstax Cnx



How To Graph Tan Ex Y Tan2x Study Com



Function Grapher And Calculator


Solution Show Me The Graph Of Y Tan2x Step By Step And How To Solve Keypoints



Graph Y Tan 2x Youtube



Drawing Trigonometric Graphs


What Is The Graph Of Mod Of Tan X Quora


Biomath Trigonometric Functions



Graph Of Y Tanx Hindi Youtube



Amplitude Period And Frequency Ck 12 Foundation



Graphs Of The Other Trigonometric Functions Algebra And Trigonometry



Transformation Of Graphs By Modulus Function Functions Openstax Cnx



What Is The Graph Of Mod Of Tan X Quora
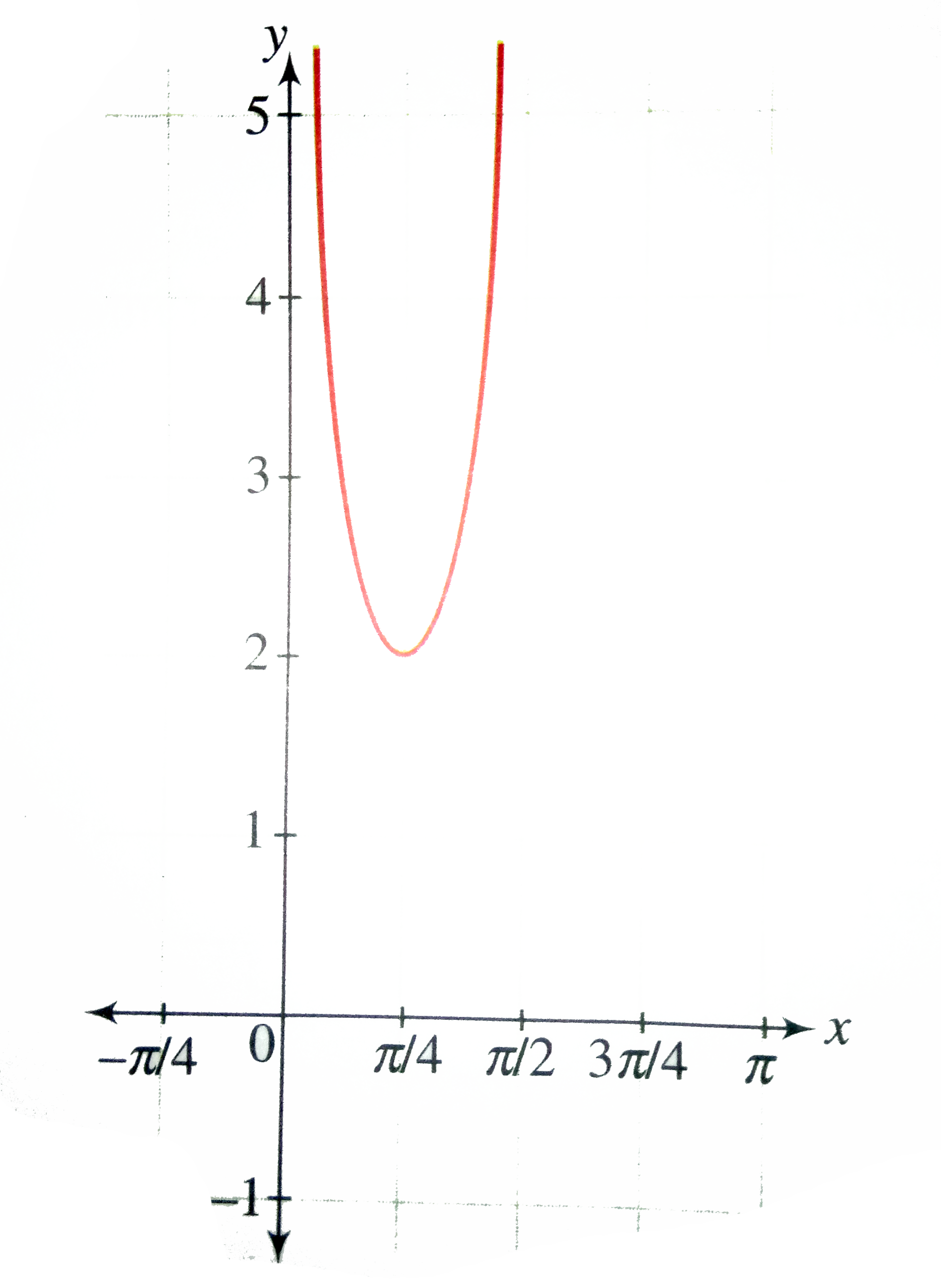


Draw The Graph Of F X Tan X Cot X


Solution Determine The Period Of Y Tan 2x


What Is The Graph Of Mod Of Tan X Quora



Compute The Area Of The Region Bounded By The Curves Y Tanx And Y



Investigating Y Sin Bx And Y Tan Bx 14murayu


Solution Determine The Period Of Y Tan 2x


Graph Tangent And Cotangent



Transformations Of Trigonometric Functions Edexcel A Level Maths Pure Revision Notes
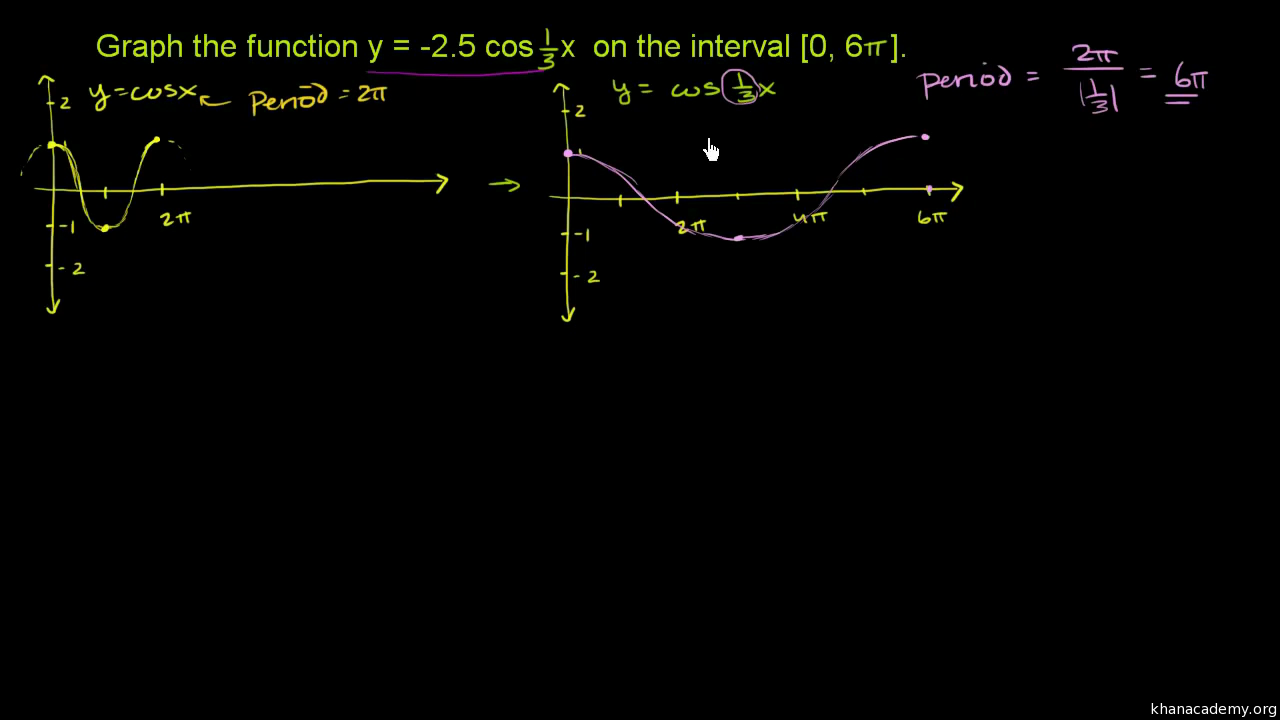


Transforming Sinusoidal Graphs Vertical Horizontal Stretches Video Khan Academy
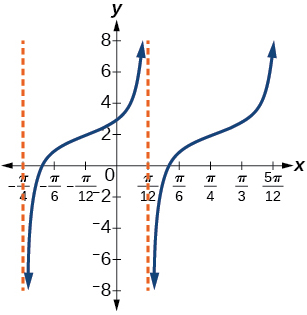


Graphs Of The Other Trigonometric Functions Algebra And Trigonometry
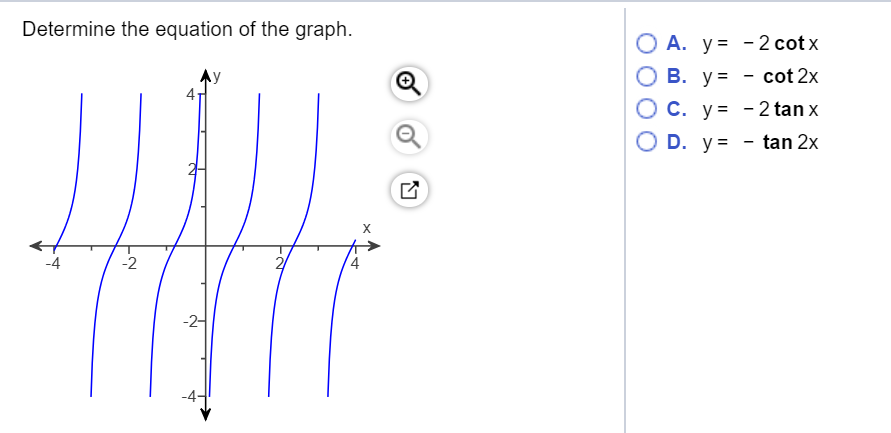


Solved Determine The Equation Of The Graph 2 Cotx Ov U Chegg Com


What Is The Graph Of Mod Of Tan X Quora
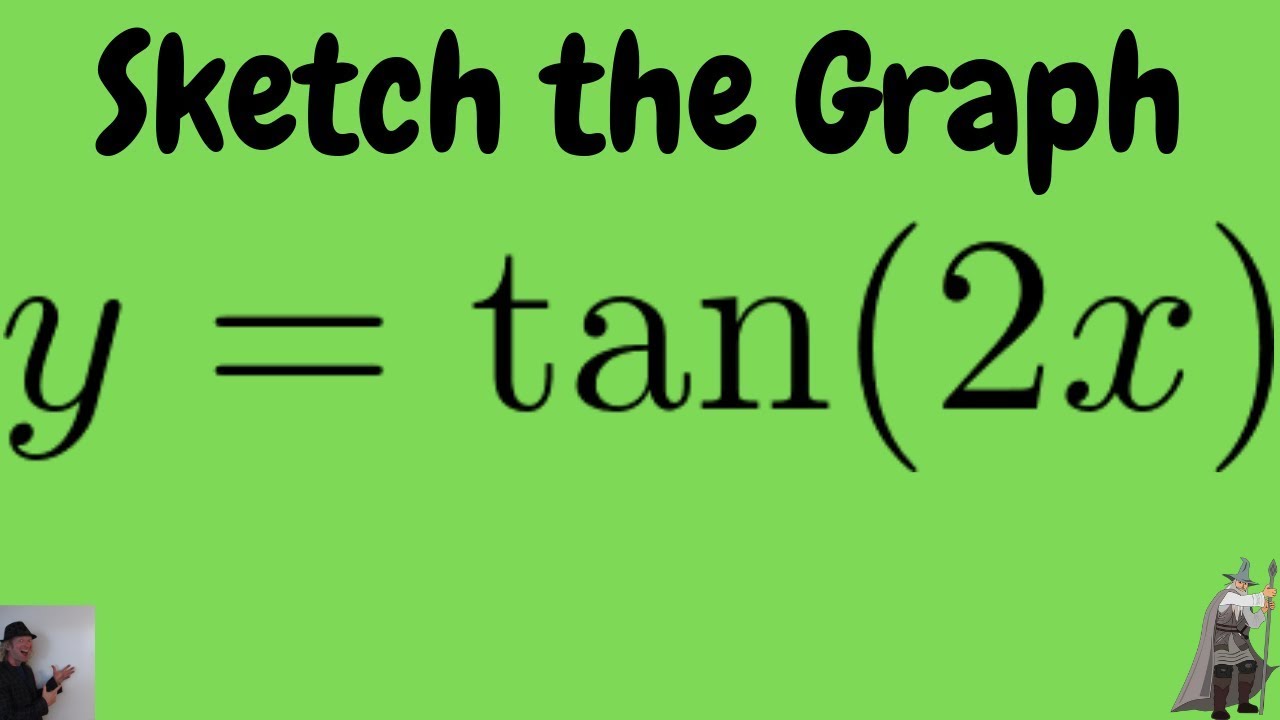


Sketch The Graph Of F X Tan 2x Youtube



The Modulus Function Mathematics Learning And Technology


Graph Tangent And Cotangent



The Tangent Function Functions Siyavula



No comments:
Post a Comment